Matplotlib defines an axes class (axis domain class). The objects of this class are called axes objects (i.e. axis domain objects). It specifies a drawing area with value range restrictions. This article will tell you how to use Matplotlib axes classes with some examples.
1. Matplotlib Axes Class Introduction.
- Multiple axes objects can be included in a given figure, but the same axes object can only be used in one figure.
- The 2D drawing area (axes) contains two axis objects. If it is a 3D drawing area, it contains three.
- By calling the add_axes() method, we can add axes objects to the canvas. This method is used to generate an axes axis domain object. The position of the object is determined by the parameter rect‘s value.
- The rect parameter is a position parameter. It accepts a floating-point number list composed of four elements, such as [left, bottom, width, height], which represents the lower-left corner coordinates (x, y), width, and height of the rectangular area added to the canvas.
ax = figure_object.add_axes([0.1,0.1,0.8,0.8])
- The value of each element is a percentage of the canvas width and height. For example, [0.2, 0.2, 0.9, 0.9], it means that painting starts from 20% of the canvas area, and the width and height is 90% of the width and height of the canvas.
1.1 Axes Class legend() Method.
- The legend() method of the axes class is responsible for drawing the legend on the canvas. It requires three parameters, as shown below.
ax.legend(handles, labels, loc) handles : It is a sequence that contains all instances of linetypes. labels : Is a string sequence that specifies the name of the label. loc : The parameter that specifies the location of the legend. The parameter value can be expressed as a string or an integer. the loc parameter's value can be one of the below list. self-adaption : best or 0. upper right : upper right or 1. upper left : upper left or 2. lower left : lower left or 3. lower right : lower right or 4. right : right or 5. center left : center left or 6. center right : center right or 7. lower center: lower center or 8. upper center : upper center or 9. center : center or 10.
1.2 Axes Class plot() Method.
- This is the basic method of the axes class, which draws the values of one array and the values of another array as lines or markers.
- The plot() method has optionally formatted string parameters that specify the linetype, marker color, style, and size.
- Color code table.
'b' : blue. 'c' : cyan. 'g' : green. 'k' : black. 'm' : magenta. 'r' : red. 'w' : white. 'y' : yellow.
- Marking symbol table.
'.' : Point mark. 'o' : Circle mark. 'x' : X mark. 'D' : Diamond mark. 'H' : Hexagon mark. 's' : Square mark. '+' : Plus sign mark
- Linetype representation character table.
'-' : Solid line. '--' : Dash line. '-.' : Dotted line. ':' : Dash line. 'H' : Hexagon mark.
2. Matplotlib Axes Example.
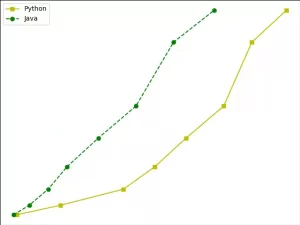
- This example will draw 2 lines with different styles using the axes class’s plot() method.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def axes_example(): # create a y axis position array. y = [2, 5, 10, 17, 26,36, 56, 66] # create 2 x axis position array. x1 = [2, 16, 36, 46, 56, 68, 77,88] x2 = [1, 6, 12, 18, 28, 40, 52, 65] # create a figure object. figure_object = plt.figure() # add the axes in the figure object. ax = figure_object.add_axes([0,0,1,1]) # draw a yellow solid curve. l1 = ax.plot(x1,y,'ys-') # draw a green circle dash curve. l2 = ax.plot(x2,y,'go--') # add a legend on the upper left corner, the legend label is Python & Java. ax.legend(labels = ('Python', 'Java'), loc = 'upper left') # show the figure. plt.show() if __name__ == '__main__': axes_example() - When you run it, you will get the below figure.